Hi! We’re glad you’re here! Ethereum is getting more mainstream nowadays and people are lining up for more Ethereum as if it was the world’s best-layered lasagna. Why is that? It is becoming more useful in Web3 and Defi.
This article will have you talking like a blockchain Ethereum layer 1 vs layer 2 expert in no time. So get another drink and stick around for a while. We will help you level up your next Ethereum conversation at the next crypto meetup.
Table of Contents
Ethereum Blockchain Technology

Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain layer platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
It consists of multiple layers, each serving a specific purpose of scaling solutions. The blockchain protocol’s base layer is preserving network security with computing power to solve cryptographic algorithms.
Blockchain Trilemma
The blockchain trilemma refers to the idea that it’s hard for blockchains to achieve optimal levels of decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously. The system throughput rate on blockchain transactions processing power gets weaker in faster-batched transaction records.
Blockchain Layer 1 VS Layer 2 Blockchain Networks

The Ethereum network’s resources, or layer 1 scaling solutions, is the original blockchain that runs on the Ethereum consensus protocol for data processing tasks. The existing architecture of blockchain layer networks of nodes that validate transactions and execute smart contracts and help with scaling solutions and data processing load state channels.
To process data simultaneously, Ethereum will automate transactions on the underlying distributed ledger of the main blockchain network. The smart contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller is directly written into lines of code.
This network processes the automatic execution of the contract without the need for intermediaries, which can save time and reduce the risk of fraud.
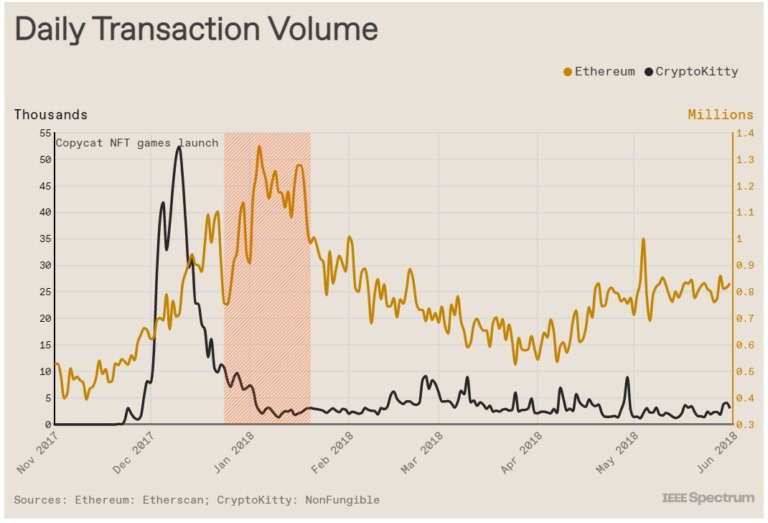
Layer 1 High Gas Fees – Spectacular Collapse Of CryptoKitties
In November 2017, the first big blockchain layer game CryptoKitties flooded the Ethereum network with users and super high gas fees. However, there was a problem with layer 1. The flood of new users created a bad user experience and bad scaling solutions.
To save the user experience of Ethereum, Layer 2 scaling solutions needed to be made.
The Ethereum main network has some limitations on scaling solutions. It can only process a limited number of transactions per second, which can lead to high transaction fees and long processing times on the layer 1 scaling solutions. This is where Ethereum layer 2 solutions come in.
Layer 2: Improved Blockchain Scalability

The consensus protocol improvements for the scaling solution is Layer 2 of Ethereum and refers to additional consensus protocols and technologies built on top of the Ethereum layer 1 blockchain.
These transaction requests protocols and technologies are designed to improve the scalability, speed, and efficiency of the Ethereum network by offloading some of the workloads from the main blockchain decentralized system. Some examples of layer 2 technologies on Ethereum include Arbitrum One, Optimism, and Boba Network.
Ethereum Layer 1 vs Layer 2: Nested Blockchain
A nested blockchain consensus protocol smart contract is essentially a blockchain within or on top of another blockchain. Nested blockchain can also be thought of as existing protocols such as layer 2.
Underlying Blockchain Protocols On Layer 1 vs Layer 2
Ethereum layer 2 can increase the transaction capacity and performance of the Ethereum main network. These solutions use off-chain transactions and other techniques to move some of the workloads off the main blockchain, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions.
Layer 2 Transaction Capacity Is Increased
Overall, the main difference between Ethereum layer 1 and layer 2 is that layer 1 is the original blockchain network, while layer 2 scaling solutions are designed to improve the performance and scalability of the network.
Layer 2 solutions are often used for high-volume and high-speed transactions, while layer 1 is used for more complex and less time-sensitive transactions.
Digging Deeper Into Layer 1

The Ethereum layer 1 scaling solutions blockchain is a decentralized, open-source platform that is powered by the native cryptocurrency Ether (ETH).
Layer 1 of Ethereum refers to the blockchain infrastructure. It is responsible for maintaining the integrity and security of the Ethereum network through the use of cryptographic protocols and consensus mechanisms.
The Ethereum layer 1 blockchain is secured by a network of nodes, which are computers that participate in the Ethereum network by validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain.
Ethereum Blockchain Networks
The Ethereum layer 1 blockchain is a decentralized, public ledger that records all transactions and smart contracts executed on the Ethereum network.
Ethereum Blockchain Network Goes To Proof Of Stake

In the Fall of 2022, Ethereum moved from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to validate and add new transactions to the blockchain. This involves validators solving complex mathematical problems to determine the validity of a transaction and earn rewards for their work.
Layer 1 Transaction Speed
Ethereum was a massive improvement over the Bitcoin blockchain to execute transactions. The processing load of the system architecture is much faster than the Bitcoin network.
The Ethereum layer 1 blockchain is secured by a network of nodes that run the Ethereum software and validate transactions. These nodes communicate with each other to reach a consensus on the state of the blockchain and prevent malicious actors from tampering with it.
Layer 1 Blockchain Layers
The Ethereum layer 1 independent blockchain networks on the blockchain are capable of executing smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
Transactions on the Ethereum layer 1 blockchain are recorded on blocks, which are added to the blockchain through the process of mining. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and earn rewards.
Layer 1 Transaction Data
The Ethereum layer 1 blockchain is not just used for financial transactions, but also for executing contracts and building decentralized applications (dApps).
One of the main advantages of the Ethereum layer 1 blockchain is its decentralized nature, which makes it resistant to censorship and tampering.
What are 3 examples of layer 1 on Ethereum?
The Ethereum main network, or “layer 1”, is the original blockchain that runs on the Ethereum protocol. It is a decentralized network of nodes that validate transaction processing tasks and execute contracts. Here are three examples of layer 1 on Ethereum:
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the runtime environment for contracts on the Ethereum main network. It is a decentralized platform that allows developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum blockchain networks.
Scaling Solutions
The Ethereum main network uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to validate transactions and secure the network. This means that transactions are validated by nodes competing to solve complex mathematical problems, which ensures that the data in the blockchain is accurate and cannot be tampered with.
Decentralized Ecosystem Underlying Blockchain Protocol
The Ethereum main network supports a wide range of blockchain networks and dApps, including decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, prediction markets, and gaming platforms. These dApps are built on top of the Ethereum main network, and they use its decentralized infrastructure to securely and transparently manage data and transactions.
Overall, the Ethereum main network, or layer 1, is the foundation of the Ethereum blockchain.
Achieve Increased Scalability With Layer 2
Layer 2 scaling solutions technologies on Ethereum are designed to improve the scalability, speed, and efficiency of the Ethereum network by offloading some of the workloads from the main blockchain.
Improved Network Security On Blockchain Networks
Layer 2 scaling solutions technologies allow for transactions and contracts to be executed off-chain, which can reduce the time and cost of executing transactions and improve the overall performance of the Ethereum network.
What are 3 examples of layer 2?
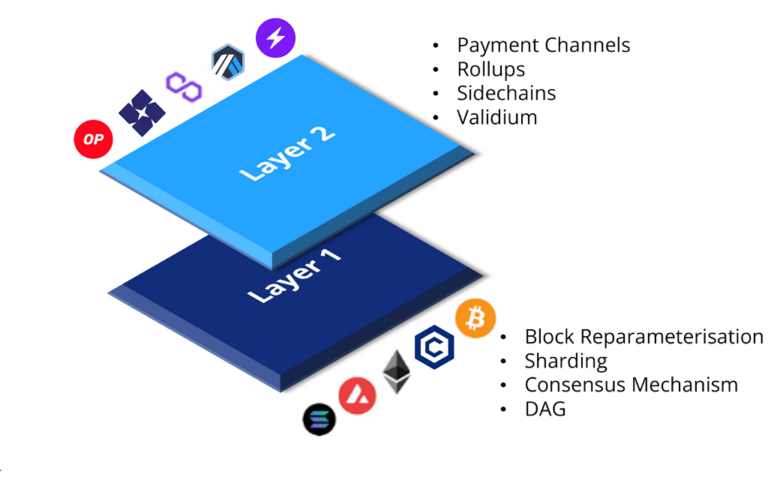
Layer 2 scaling solutions use off-chain transactions and other techniques to move some of the workloads off the main blockchain, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions and relieving network congestion. Here are three examples of layer 2 on Ethereum:
Arbitrum One Blockchain Technology
Arbitrum is an Optimistic Rollup that aims to give the user an experience exactly like interacting with Ethereum, but with transactions costing a fraction of what they do on L1. It has its ecosystem of DAPPS, bridges, and even its blockchain explorer.
Optimism Blockchain Protocol
Optimism is a low-cost, fast, simple, and secure EVM-equivalent optimistic rollup. It claims to give the Ethereum experience at 10X the speed. It scales Ethereum’s tech while also scaling solutions and its values through retroactive public goods funding.
Boba Network Blockchain Protocol
Boba Network is an optimistic rollup and is another layer 2 scaling solution that allows for the batching and bundling of multiple transactions into a single transaction, which can be processed more efficiently on the main Ethereum blockchain.
Optimistic Rollups Blockchain Protocol
The Optimistic Rollup is a layer 2 solution that allows for the execution of contracts on the Ethereum main network, without the need for the entire network to process each transaction. This can significantly improve the performance and scalability of the Ethereum network, and it allows for more complex and sophisticated dApps to be built on top of the Ethereum main network.
Lightning Network – Layer 2 On Bitcoin

Bitcoin has a layer 2 called the lightning network. Transactions performed on the lightning network are lighter, which can also be thought of as a lighting network because it makes the entire transaction set lighter on state channels.

In summary, layer 1 is the foundational layer of Ethereum that provides the underlying blockchain infrastructure, while layer 2 consists of additional protocols and technologies built on top of the layer 1 blockchain to improve its scalability and efficiency.






